Facebook添加双重验证
在 Facebook(Meta)账户上启用双重验证(2FA) 以提升安全性。主要内容包括:
双重验证的作用:防止未经授权的登录,即使密码泄露也能保护账户。
设置步骤:通过手机短信、验证器应用(如 Google Authenticator)或物理安全密钥绑定 2FA。
备用方法:生成一次性备用代码,避免设备丢失时无法登录。
注意事项:建议绑定多设备并妥善保存备用代码,以防锁定账户。
在 Facebook(Meta)账户上启用双重验证(2FA) 以提升安全性。主要内容包括:
双重验证的作用:防止未经授权的登录,即使密码泄露也能保护账户。
设置步骤:通过手机短信、验证器应用(如 Google Authenticator)或物理安全密钥绑定 2FA。
备用方法:生成一次性备用代码,避免设备丢失时无法登录。
注意事项:建议绑定多设备并妥善保存备用代码,以防锁定账户。
Shopify 结账页面的国际运费设置问题,主要针对非美国地址无法正确计算运费的情况。
问题描述:用户填写非美国地址后,运费无法正常显示或设置失败。
解决方案:
在 Shopify 后台 设置 > 配送 中添加目标国家/地区,并绑定运费规则。
检查是否启用自动运费计算(如 Shopify Shipping 或第三方物流集成)。
1 | let i = 0 |
SetTimeout在for循环之后才执行,那时候i为6,然后再打印出6次6
1 | for(let i = 0; i<6; i++){ |
1 | let i = 0 |
1 | let i = 0 |
1 | let i = new Array(6).fill('') |
1 | let i = 0 |
1 | $(document) //选择整个文档对象 |
1 | $('a:first') //选择网页中第一个a元素 |
1 | $('div').find('h3').eq(2).html('Hello'); |
分解开来,就是下面这样:
1 | $('div') //找到div元素 |
jQuery还提供了.end()方法,使得结果集可以后退一步:
1 | $('div') |
1 | $('<p>Hello</p>'); |
假定我们选中了一个div元素,需要把它移动到p元素后面。
第一种方法是使用.insertAfter(),把div元素移动p元素后面:
1 | $('div').insertAfter($('p')); |
第二种方法是使用.after(),把p元素加到div元素前面:
1 | $('p').after($('div')); |
1 | $('h1').html(); //html()没有参数,表示取出h1的值 |
常见的取值和赋值函数如下:
1 | .html() 取出或设置html内容 |
捕获型事件(event capturing):事件从最不精确的对象(document 对象)开始触发,然后到最精确(也可以在窗口级别捕获事件,不过必须由开发人员特别指定)
冒泡型事件:事件按照从最特定的事件目标到最不特定的事件目标(document对象)的顺序触发。
w3c规定了,任何发生在w3c事件模型中的事件,首是进入捕获阶段,直到达到目标元素,再进入冒泡阶段。绑定在被点击元素的事件是按照代码的顺序发生的。
冒泡,它就像鱼儿吐泡泡一样,从下到上。
从祖先元素开始慢慢找,最后找到我们的点击目标,这个行为不就像警察叔叔抓坏人一样,逐渐的缩小抓捕范围,最后确定到某一个人身上,所以这个叫做捕获。
事件委托还有一个名字叫事件代理,JS高程上讲:事件委托就是利用事件冒泡,只制定一个时间处理程序,就可以管理某一类型的所有事件。我用取快递来解释这个现象: 有三个同事预计会在周一收到快递。为签收快递,有两种办法:一是三个人在公司门口等快递;二是委托给前台代为签收。现实当中,我们大都采用委托的方案。前台收到快递后,她会判断收件人是谁,然后按照收件人的要求签收,甚至代为付款。这种方案还有一个优势,那就是即使公司里来了新员工(不管多少),前台也会在收到寄给新员工的快递后核实并代为签收。
M:model(模型) 负责操作数据与服务器的交互,将请求到的数据传给control
V:View (视图) 负责所有UI界面,比如el,templete,render
C:controller(控制器)负责其他,比如初始化和事件,负责监听和处理View事件,并更新和调用 Model,负责监听Model数据变化,并更新View
1 | /** 模擬 Model, View, Controller */ |
1 | _self.getEventBus |
Table-Driven Approach
解决if else面对多种情况的情形,以表的形式进行获取数据,通过下标索引来查
1 | methods{ |
模块化就是把一个模块的代码放在一个文件夹里,再进行引入,简化了代码之间的影响
1 | let string=`内容` |
如果 .parent 的 height 不写,你只需要 padding: 10px 0; 就能将 .child 垂直居中;
如果 .parent 的 height 写死了,就很难把 .child 居中,以下是垂直居中的方法。
忠告:能不写 height 就千万别写 height。
代码
1 | // html |
1 | .parent{ |
效果图
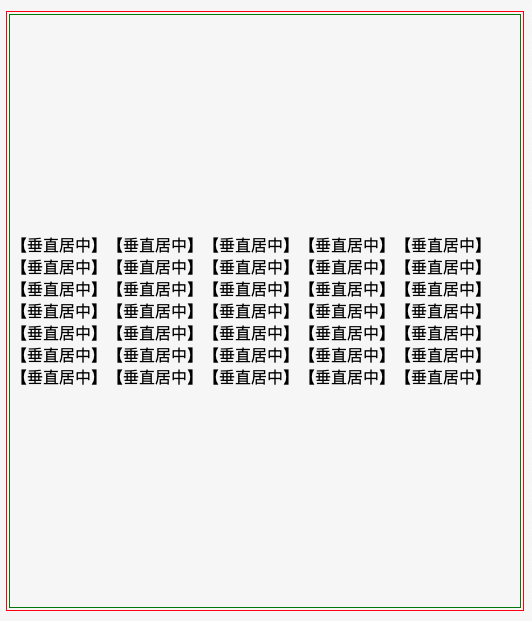
代码
1 | // html |
1 | .parent{ |
效果图
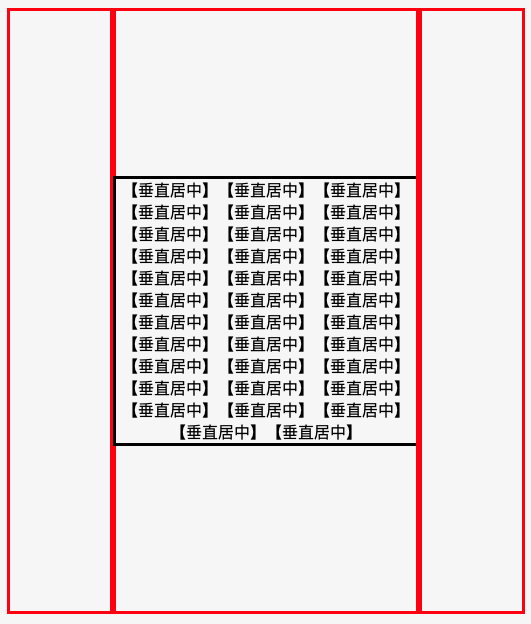
优化版
1 | // html |
1 | .parent{ |
代码
1 | // html |
1 | // css |
效果图
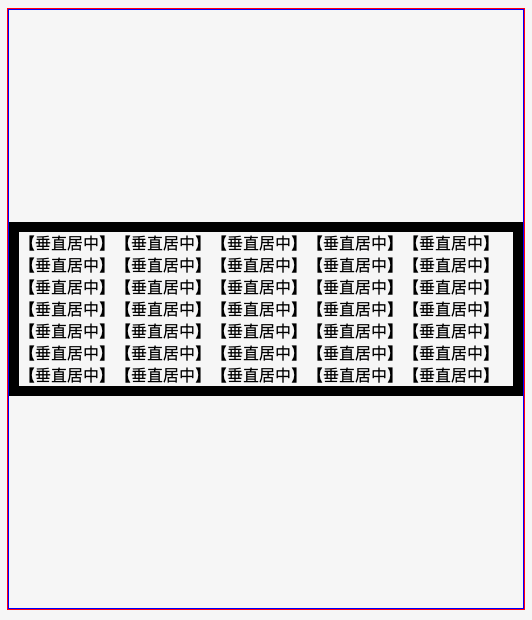
代码
1 | // html |
1 | // css |
效果图

代码
1 | // html |
1 | // css |
效果图

代码
1 | // html |
1 | // css |
效果图
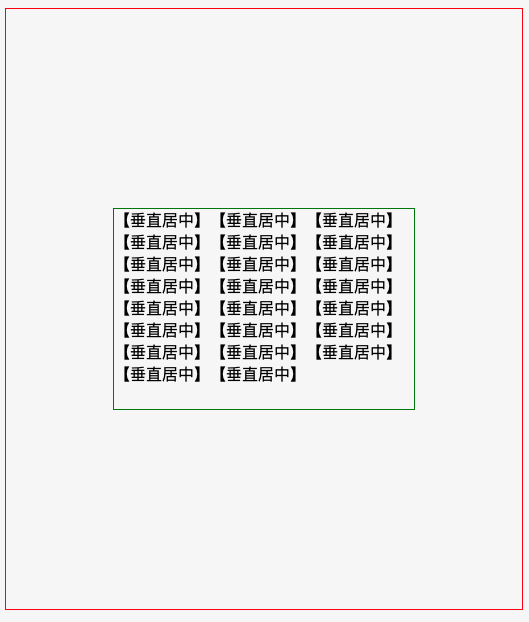
代码
1 | <!DOCTYPE html> |
1 | // css |
效果图



代码
1 | <body> |
1 | .child1,.child2,.friend{ |
代码
1 | <body> |
1 | .child1,.child2,.friend{ |
效果图

代码
1 | <body> |
1 | .child1,.child2,.friend{ |
效果图
